Your Login Attempt Was Not Successful Try Again Spring Boot
Learn to add together Jump security login form to any spring web applications using detailed information discussed in spring security tutorial.
Table of Contents one. Background information 2. Spring security maven dependencies three. Configure DelegatingFilterProxy in web.xml 4. Add together security configuration in awarding-security.xml v. Update the controller 6. Add related JSP views vii. Test the application
Read More than : Spring security 5 login form example [Updated for Leap 5]
1. Background information
We learned to integrate between Spring 3 and hibernate in linked mail. That awarding was simple web application which presents a view where user can add/edit employees.
Lets secure that awarding. The scope of this tutorial is to:
- Just authorized user should exist able to admission edit employee screen.
- Unauthorized users should be presented with login screen.
- Successful credentials should forward to edit employee screen.
- Unsuccessful credentials should forward to access denied screen.
- At that place should be a link for logout of the application.
two. Spring security maven dependencies
Lets commencement with very offset step i.due east. update the project dependencies. It will add post-obit four sub-modules in demo for post-obit reasons:
- spring-security-cadre : It contains cadre hallmark and admission-command classes and interfaces.
- spring-security-spider web : It contains filters and related web-security infrastructure code. It as well enable URL based security which we are going to use in this demo.
- leap-security-config : It contains the security namespace parsing code. You need information technology if you are using the Spring Security XML file for configuration.
- spring-security-taglibs : Information technology provides basic support for accessing security information and applying security constraints in JSPs.
<properties> <org.springframework.version>iii.0.5.RELEASE</org.springframework.version> </backdrop> <!-- Bound Security --> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.security</groupid> <artifactid>jump-security-core</artifactid> <version>${org.springframework.version}</version> <type>jar</type> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.security</groupid> <artifactid>spring-security-web</artifactid> <version>${org.springframework.version}</version> <type>jar</type> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.security</groupid> <artifactid>spring-security-config</artifactid> <version>${org.springframework.version}</version> <type>jar</type> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.security</groupid> <artifactid>spring-security-taglibs</artifactid> <version>${org.springframework.version}</version> <type>jar</type> <scope>compile</telescopic> </dependency> Now apply "mvn compile" command to update the dependencies in project.
3. Configure DelegatingFilterProxy in web.xml
Spring Security'due south web infrastructure is based entirely on standard servlet filters. These filters are defined in web.xml file or they will be ignored by the servlet container.
In Leap Security, the filter classes are also Spring beans defined in the application context and thus able to take advantage of Spring's rich dependency-injection facilities and lifecycle interfaces. Spring's DelegatingFilterProxy provides the link between web.xml and the application context.
<filter> <filter-proper noun>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-course>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
If y'all are non using any explicit filter definitions and wants bound to configure basic infrastructure for you, and then use filter proper noun as 'springSecurityFilterChain' every bit in above instance. Note that y'all should not use this bean proper name yourself. Once you've added this to your web.xml, y'all're set to start editing your spring security configuration file. Spider web security services are configured using the element.
Too practice not forget to put security configuration file in context config location setting.
<context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value> /Spider web-INF/employee-servlet.xml /WEB-INF/application-security.xml </param-value> </context-param>
A consummate web.xml file will expect similar this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://coffee.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.dominicus.com/xml/ns/javaee https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/; id="WebApp_ID" version="2.v"> <display-proper noun>Classic Created Web Application</brandish-proper name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>/WEB-INF/index.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-listing> <filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-proper noun> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-proper name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <servlet> <servlet-name>employee</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>employee</servlet-proper name> <url-design>/</url-blueprint> </servlet-mapping> <context-param> <param-proper name>contextConfigLocation</param-proper noun> <param-value> /Web-INF/employee-servlet.xml /WEB-INF/application-security.xml </param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-form>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-grade> </listener> </web-app>
4. Configure login logout security
Every bit nosotros learned in last department that using filter name every bit springSecurityFilterChain can assistance you configure the bones infrastructure using element. Lets see how it is configured first? I have written a basic configuration for this demo:
<?xml version="ane.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security" xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://world wide web.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://world wide web.springframework.org/schema/beans/leap-beans-iii.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.0.iii.xsd"> <http auto-config="truthful" utilize-expressions="true"> <intercept-url pattern="/login" access="permitAll" /> <intercept-url pattern="/logout" access="permitAll" /> <intercept-url design="/accessdenied" access="permitAll" /> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')" /> <grade-login login-page="/login" default-target-url="/listing" authentication-failure-url="/accessdenied" /> <logout logout-success-url="/logout" /> </http> <authentication-director alias="authenticationManager"> <authentication-provider> <user-service> <user name="lokesh" password="countersign" authorities="ROLE_USER" /> </user-service> </authentication-provider> </hallmark-director> </beans:beans> Lets see what this configuration really mean.
-
http: Include configuration related url level security. This element is the parent for all spider web-related namespace functionality. -
auto-config: Includes some bones services. It is shorthand for –<http> <form-login /> <http-basic /> <logout /> </http>
-
use-expressions: It is here to employ expressions to secure individual URLs. These expressions can be e.g.hasRole([part]),hasAnyRole([role1,role2]),permitAll,denyAlletc. -
intercept-url: This will lucifer the requested url pattern from request and will decide what action to have based on access value. -
form-login: This will come into moving-picture show when user will try to admission whatever secured URL. A login page mapped to "login-page" aspect will exist served for authentication check. Information technology is spring security login-processing-url.If non provided, spring volition provide an inbuilt login page to user. It also contains attribute for default target if login success, or login failure due to invalid user/countersign friction match.
-
logout: This will help to notice the side by side view if logout is called in application.
I am using XML based user service i.east. I will non go to database for countersign validation rather I have stored username/password combination in configuration file itself. To use this king of setup, authentication-manager is setup with inline in-congenital user details service. In more than real time applications, this is going to be some user service fetching data from remote database.
v. Jump controller
I will reuse the controller and will add boosted mappings and handler methods in controller. These boosted URLs are /login, /logout and /accessdenied. The updated controller having all method handlers looks similar this:
bundle com.howtodoinjava.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.note.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap; import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.notation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import com.howtodoinjava.entity.EmployeeEntity; import com.howtodoinjava.service.EmployeeManager; @Controller public class EditEmployeeController { @Autowired private EmployeeManager employeeManager; public void setEmployeeManager(EmployeeManager employeeManager) { this.employeeManager = employeeManager; } @RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.Become) public Cord login(ModelMap model) { render "login"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/accessdenied", method = RequestMethod.Become) public String loginerror(ModelMap model) { model.addAttribute("error", "true"); return "denied"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/logout", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String logout(ModelMap model) { return "logout"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String defaultPage(ModelMap map) { render "redirect:/list"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/list", method = RequestMethod.Go) public String listEmployees(ModelMap map) { map.addAttribute("employee", new EmployeeEntity()); map.addAttribute("employeeList", employeeManager.getAllEmployees()); return "editEmployeeList"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/add together", method = RequestMethod.Mail service) public Cord addEmployee( @ModelAttribute(value = "employee") EmployeeEntity employee, BindingResult result) { employeeManager.addEmployee(employee); return "redirect:/listing"; } @RequestMapping("/delete/{employeeId}") public String deleteEmplyee(@PathVariable("employeeId") Integer employeeId) { employeeManager.deleteEmployee(employeeId); return "redirect:/list"; } } 6. Spring views
We have at present configured our application with security configuration and controller handlers. Its fourth dimension to write the views which are substantially JSP files. Most of import addition in jsp files is login.jsp file.
This file have the grade which contains text boxes for username and countersign field. Lets see how information technology is written:
half-dozen.one. login.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.lord's day.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <%@ taglib uri="http://world wide web.springframework.org/tags/course" prefix="class" %> <%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring" %> <html> <body> <h1 id="banner">Login to Security Demo</h1> <form proper noun="f" action="<c:url value='j_spring_security_check'/>" method="Mail"> <table> <tr> <td>Username:</td> <td><input type='text' proper name='j_username' /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Password:</td> <td><input type='password' proper noun='j_password'></td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="2"> </td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan='ii'><input name="submit" blazon="submit"> <input name="reset" blazon="reset"></td> </tr> </table> </form> </body> </html>
By default, jump auto generates and configures a UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter bean. This filter, by default, responds to the URL /j_spring_security_check when processing a login POST from your spider web-course. For username field it uses 'j_username' and for password field it uses 'j_password'.
On submitting this form, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter will lucifer the username and password as configured in hallmark-provider settings in application-security.xml.
half dozen.two. logout.jsp
< % session.invalidate(); %> You are now logged out!! <a href="//howtodoinjava.com/spring/spring-security/login-form-based-spring-3-security-example/">go back</a>
This view but invalidate the session and provide a link to go dorsum to login page.
6.three. denied.jsp
This jsp file volition come up in user screen when user will try to authenticate with invalid user proper noun and password combinations. It volition show the corresponding message as configured in bulletin.properties in your classpath.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%> <html> <body> <h1 id="banner">Unauthorized Access !!</h1> <hr /> <c:if test="${non empty error}"> <div fashion="color:cherry-red"> Your fake login attempt was bursted, dare again !!<br /> Acquired : ${sessionScope["SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION"].message} </div> </c:if> <p form="message">Access denied!</p> <a href="//howtodoinjava.com/spring/spring-security/login-form-based-leap-3-security-example/">Go back to login page</a> </torso> </html> 7. Leap security login grade demo
Its fourth dimension to exam the application. Simply deploy the application in any server e.g. in my case i am using Tomcat 7.0. Now, do post-obit steps:
seven.one. Type the URL in browser "http://localhost:8080/Spring3HibernateIntegration"
It volition bring the login screen as besides /login, /logoutand /accessdenied all other URLs are protected URLs.

7.ii. Endeavour to authenticate with username 'demo' and password '1234'

It will given access denied fault considering username and password is invalid.
7.three. Try to authenticate with username 'lokesh' and password 'password'
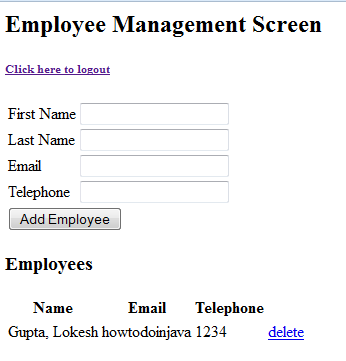
It will given employee management screen because username and password is correct.
7.4. Click on logout link

User will be logged out and login screen will appear.
I hope this leap mvc login example has been able to put some light on basic jump security machinery using xml configurations. If you any question on this Spring security login class case, drop me a comment.
Happy Learning !!
Source: https://howtodoinjava.com/spring-security/login-form-based-spring-3-security-example/
Postar um comentário for "Your Login Attempt Was Not Successful Try Again Spring Boot"